Last Updated: Dec 1, 2025

You probably learned in school that iron is an important mineral for your body. But when your water has a high concentration, it can cause issues. We’ll explain the issues and how to eliminate them from your home. Let’s dive in!
What Causes Orange Water Stains in Your Home?

Iron is an abundant element in the Earth’s crust. It dissolves in water from contact with iron-bearing soil and rock (especially common with well water). Iron in your water usually takes two forms:
- Ferrous iron (soluble): Water is clear when it first comes out of the tap because the iron is completely dissolved.
- Ferric iron (insoluble): When ferrous iron is exposed to air (oxidation), it turns cloudy. It forms the reddish-brown, insoluble sediment known as rust. This causes the color in your sink, bathtub, or laundry.
Other Potential Causes of Iron-like Staining (Non-Iron):
- Magnesium: High levels of magnesium can combine with soap scum to form tough orange deposits.
- Corroding pipes: Rust can also result from the corrosion of iron or steel well casings or older plumbing pipes.
- Washing machine: Older washing machines can have internal rust that transfers to laundry.
- Pink mold: An airborne bacterium that grows in damp, moist environments. Often appearing reddish or orange. While not a true mold, it requires addressing due to potential health issues.
Signs of Excessive Iron in Your Water Supply
Since iron can be dissolved in water at first, here are some ways to know if there’s too much.
- Visible stains:
- Reddish-brown, yellow, or orange stains on tubs, sinks, toilets, plates, and utensils.
- Discolored clothing and dark stains on clothes after washing.
 Water appearance and smell:
Water appearance and smell:
- Water initially looks clear, but reddish-brown particles appear after standing.
- Appears rusty or red/yellow immediately.
- Metallic taste due to the high amount of dissolved iron
- Musty or earthy smell (or “rotten eggs” smell if sulfur is in it as well).
- Impact on the home:
- Clogged or rusting pipes/fixtures reduce water flow, potentially leading to leaks.
- Impact on eating and drinking:
- Tea, coffee, and other beverages may have an inky, black appearance and a harsh taste.
- Food cooked in the water may taste bitter or become discolored.
- Impact on your body:
- Dry, itchy skin due to iron interfering with natural oils and soap residue.
- Acne and clogged pores (iron can promote bacterial/fungal growth).
- Brittle, discolored hair (iron can damage keratin, important for strong hair).
Health Concerns Related to Iron and Other Water Contaminants
While minor iron buildup is often harmless, high levels for long periods may cause problems. Note: We are water treatment experts and not medical professionals. If you have concerns about iron toxicity or overload, please consult your doctor.
- Iron (overload/toxicity):
-
- Extremely high or prolonged intake may hurt internal organs, increase fatigue, and cause joint pain.
- Studies also link excess iron to potential DNA damage. It can increase the risk of infections, as iron is a nutrient for bacteria (including E. coli).
- Pink mold/bacteria:
- While not as severe as black mold, pink mold can cause health issues ranging from allergic reactions to lung issues.
- Copper:
- Iron is the typical cause of orange/brown stains. Blue or greenish staining is a distinct problem caused by excessive copper. This can be caused by corrosion from acidic water. Testing is required for both iron and copper contamination.
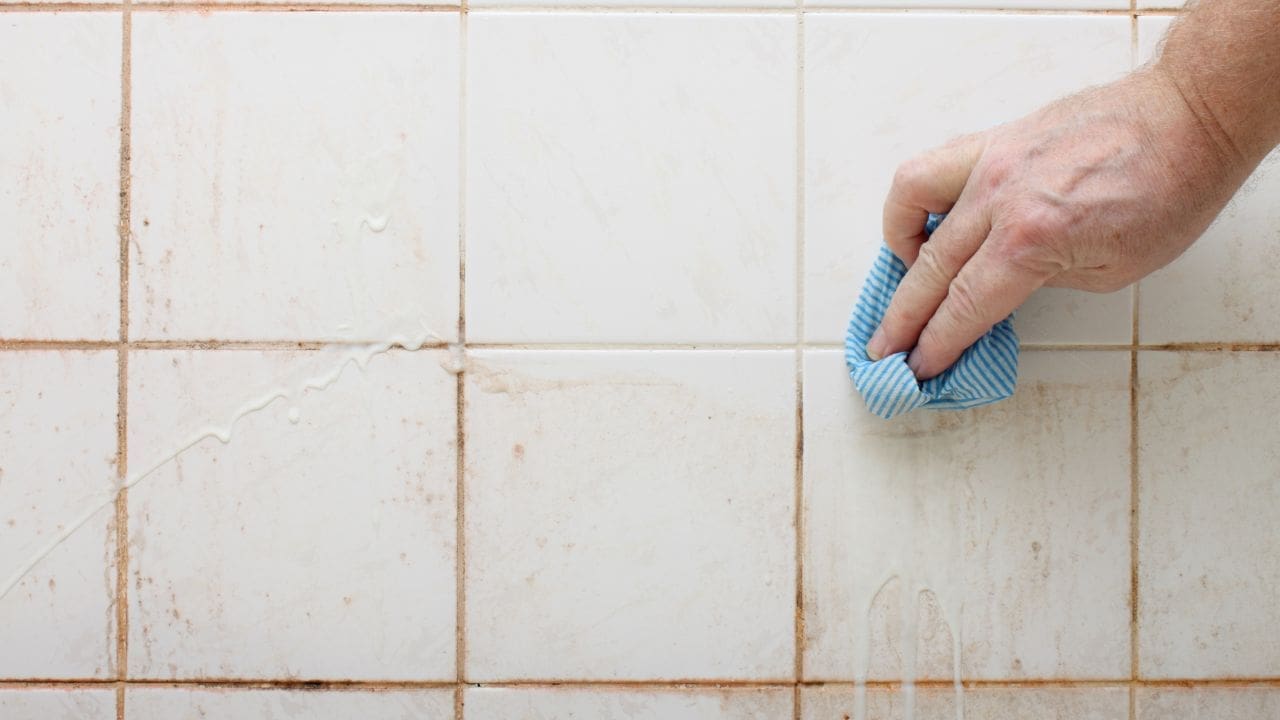
How to Remove Existing Orange Water Stains (Temporary Fixes)
Once you notice these stains, it’s time to take action. However, many homeowners struggle to remove these stains simply by scrubbing them away. There are a few ways you can get rid of orange water stains once they settle into your home.
 DO NOT use bleach: Bleach is an oxidizer and will worsen iron/rust stains by promoting oxidation.
DO NOT use bleach: Bleach is an oxidizer and will worsen iron/rust stains by promoting oxidation.- Use a recommended stain remover:
- Removers: Use commercial products containing strong acids like oxalic acid.
** Always follow label instructions and wear protective gear. - Treating clothes: Use oxalic acid or homemade mixtures of hydrogen peroxide and vinegar for fabrics.
- Homemade solutions for fixtures/surfaces:
- Baking soda and white vinegar: Mix a two-part vinegar/one-part water solution. Spray and let sit (20 mins), then scrub with baking soda.
- Lemon juice and water: Combine and spray on stains, let sit (10 mins), then clean.
- Removers: Use commercial products containing strong acids like oxalic acid.
Preventing Stains with Water Treatment Systems (Permanent Solution)
Now that you have taken care of the visible effects of the iron, you will want to prevent them from coming back.
- Start with water testing: Prevention begins with a thorough Free Water Analysis. This will help identify the form and amount of iron. It can also identify other contaminants. With WQA Certification and decades of experience, C and J Water is uniquely qualified to diagnose and treat any hard water and contamination issues.
Removal and filtration (targets high iron and pathogens):
- AIO (Air Induction Oxidation) Systems:
- Utilizes natural oxidation (air) within the system to convert ferrous iron to ferric iron. This can be filtered out without using chemicals. Removes iron and odor.
- Reverse Osmosis (RO) filtration:
- Designed for drinking and cooking water. Removes up to 99% of dissolved solids not removed by a softener. Excess iron, arsenic, lead, and chromium are also removed.
- UV Light (pathogen removal):
- Aids in removing living pathogens (bacteria and viruses) from the water supply.
- Sediment filter: Removes large particles and protects the lifespan of treatment equipment.
Well water maintenance:
- Well cleaning: For private wells, professional cleaning every 10 years is important. This prevents rust buildup and keeps the system in good order.
Water softener systems (target hard minerals & dissolved iron):
A softener isn’t the first line of defense, but it can help remove low to moderate levels of dissolved iron.
- Single-Tank Water Softener: Most common for city water, regenerates overnight.
- Twin-Tank Softener: Provides 24/7 soft water because one tank is always online while the other regenerates using soft water. This helps clean the iron from the resin bed.
- Softener/Dechlorinator combo: Extends the life of the softener, removes chlorine and other irritants.
Ready to Solve Your Water Quality Problems?
C and J Water has helped thousands of Central Indiana families treat their water. We can help you too. Don’t tolerate ugly stains or risk health issues from contaminated water. C and J Water provides comprehensive water solutions and expertise. Contact us today to schedule your free analysis and discover the right system for your home.